Digital Signatures
Digital Signatures
Digital Signatures
Digital Signatures Explained: Ensuring Document Security in a Paperless World
Digital Signatures Explained: Ensuring Document Security in a Paperless World
Digital Signatures Explained: Ensuring Document Security in a Paperless World
28 Jan 2025
28 Jan 2025
28 Jan 2025
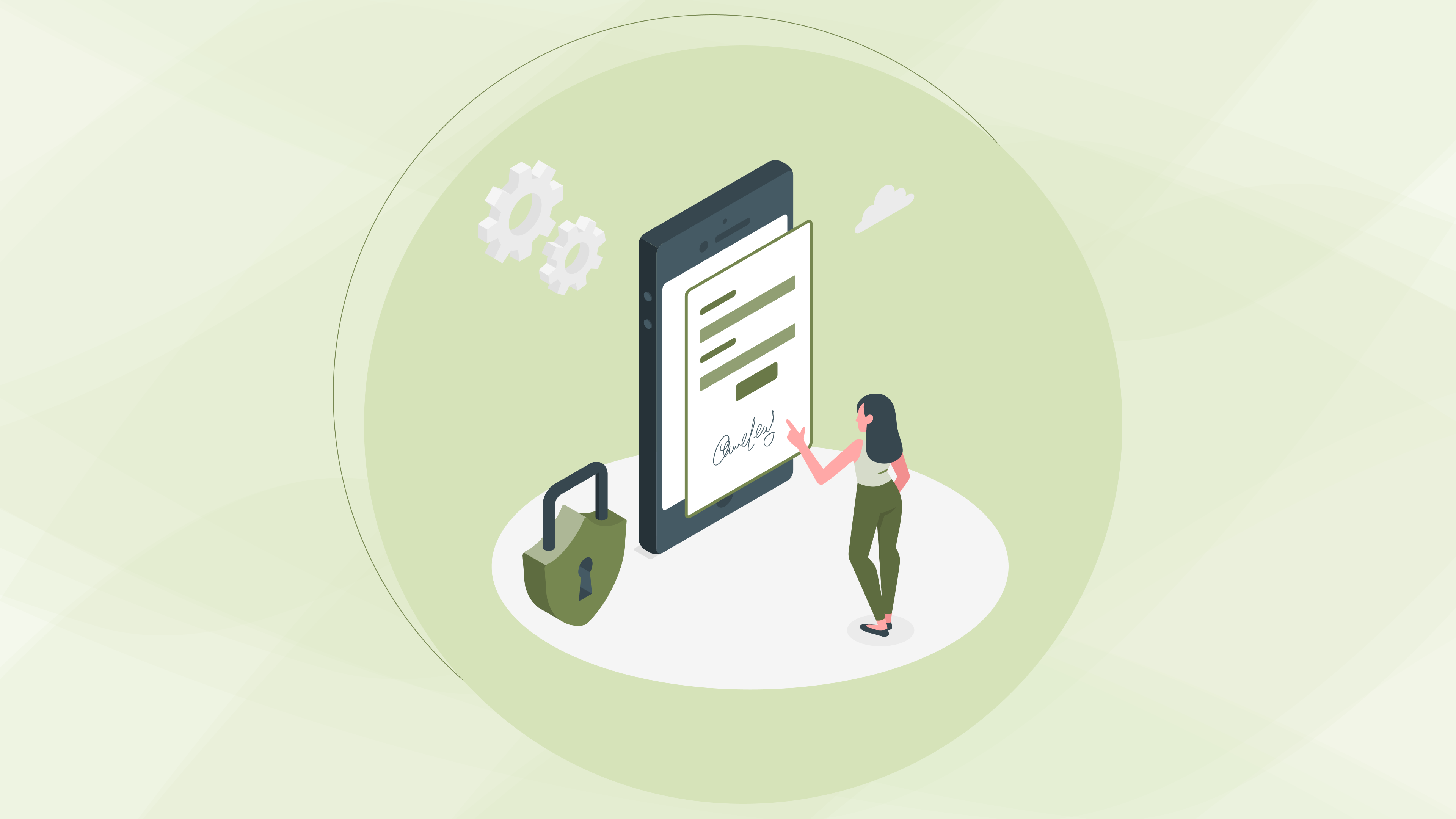



What is a Digital Signature?
In an increasingly paperless world, digital signatures are revolutionizing the way we authenticate documents and messages. These electronic signatures serve as a secure, tamper-proof method for verifying the origin and content of digital information. By leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques, digital signatures provide a reliable means of maintaining trust and security, ensuring that documents remain authentic and unaltered throughout their lifecycle.
How Do Digital Signatures Work?
Understanding how digital signatures function requires a closer look at the cryptographic techniques that make them secure and trustworthy. These signatures rely on a combination of public and private keys, along with hashing algorithms and encryption methods, to ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital content.
Key Pair Generation
Each user is issued a unique pair of cryptographic keys: a private key, which is confidential, and a public key, which is shared with others. This pair works together to create and verify digital signatures, ensuring security and authenticity.
Hashing Algorithm
Before a document is signed, its contents are processed through a hashing algorithm, which generates a unique fixed-length hash value. Any alteration to the document’s content results in a completely different hash value, safeguarding the document’s integrity.
Encryption with Private Key
The hash value generated from the document is encrypted using the signer’s private key, creating the digital signature. This ensures that only the signer could have created the signature, verifying its authenticity.
Verification Process
To verify a digital signature, the recipient decrypts the signature using the signer’s public key. They then generate a new hash from the document and compare it to the decrypted hash. If the two hashes match, the document is confirmed as authentic and unchanged.
How Digital Signatures Ensure Paperless Security
Digital signatures employ a combination of cryptographic principles and trusted entities to ensure secure, paperless transactions. Here’s how these elements contribute to their effectiveness:
Public Key and Private Key
The use of a private key for creating the signature and a public key for verification ensures that documents remain secure and that the authenticity of the signer is upheld without compromising sensitive information.
Certificate Authority (CA)
Certificate Authorities play a vital role by issuing digital certificates that link a signer’s identity to their public key. These certificates verify the authenticity of the signer and protect against impersonation, ensuring trust in the system.
Digital Fingerprint
A hash value acts as a unique digital fingerprint for the document. Any modification to the document invalidates this fingerprint, ensuring that tampering is immediately detectable.
Hashing Algorithm
Advanced hashing algorithms like SHA-256 transform data into a secure, fixed-length representation. These algorithms are irreversible, which means it is impossible to reconstruct the original data from the hash value, ensuring the document’s security.
Encryption and Decryption
The encryption of the hash value with the signer’s private key creates the digital signature, while decryption using the public key allows recipients to verify the document’s authenticity and integrity.
Benefits of Using Digital Signatures
Digital signatures offer numerous advantages that make them indispensable in a paperless world. By streamlining processes and ensuring security, they are transforming how organizations and individuals manage their digital transactions.
Enhanced Security
Digital signatures provide unparalleled security by ensuring data integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. The use of encryption and hashing makes them tamper-proof and resistant to fraud, providing confidence in their validity.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Eliminating the need for physical documents reduces costs associated with printing, signing, and shipping. Additionally, digital signatures enable instant approvals and transactions, saving time for all parties involved.
Eco-Friendly
By reducing reliance on paper, ink, and physical transportation, digital signatures contribute to environmental sustainability. They help organizations align with global eco-friendly practices and reduce their carbon footprint.
Legal Validity
Digital signatures are legally recognized under various regulations, including the eSign Act (USA), eIDAS (EU), and IT Act (India). This ensures that they are compliant and trustworthy for signing contracts, legal documents, and more.
Scalability
Whether it’s signing contracts, securing emails, or authenticating software, digital signatures can scale to meet the needs of individuals, small businesses, and large enterprises alike, offering versatility across applications.
Conclusion
In a world that is rapidly embracing digital transformation, digital signatures have become an essential tool for ensuring secure and authentic paperless transactions. By combining cryptographic techniques with trusted certificate authorities, digital signatures offer a reliable, efficient, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods of signing and verifying documents.
Understanding and adopting digital signatures will empower organizations and individuals to confidently navigate the digital landscape. Whether you’re signing contracts, verifying identities, or securing sensitive data, digital signatures provide the foundation for a secure and seamless digital future.
What is a Digital Signature?
In an increasingly paperless world, digital signatures are revolutionizing the way we authenticate documents and messages. These electronic signatures serve as a secure, tamper-proof method for verifying the origin and content of digital information. By leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques, digital signatures provide a reliable means of maintaining trust and security, ensuring that documents remain authentic and unaltered throughout their lifecycle.
How Do Digital Signatures Work?
Understanding how digital signatures function requires a closer look at the cryptographic techniques that make them secure and trustworthy. These signatures rely on a combination of public and private keys, along with hashing algorithms and encryption methods, to ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital content.
Key Pair Generation
Each user is issued a unique pair of cryptographic keys: a private key, which is confidential, and a public key, which is shared with others. This pair works together to create and verify digital signatures, ensuring security and authenticity.
Hashing Algorithm
Before a document is signed, its contents are processed through a hashing algorithm, which generates a unique fixed-length hash value. Any alteration to the document’s content results in a completely different hash value, safeguarding the document’s integrity.
Encryption with Private Key
The hash value generated from the document is encrypted using the signer’s private key, creating the digital signature. This ensures that only the signer could have created the signature, verifying its authenticity.
Verification Process
To verify a digital signature, the recipient decrypts the signature using the signer’s public key. They then generate a new hash from the document and compare it to the decrypted hash. If the two hashes match, the document is confirmed as authentic and unchanged.
How Digital Signatures Ensure Paperless Security
Digital signatures employ a combination of cryptographic principles and trusted entities to ensure secure, paperless transactions. Here’s how these elements contribute to their effectiveness:
Public Key and Private Key
The use of a private key for creating the signature and a public key for verification ensures that documents remain secure and that the authenticity of the signer is upheld without compromising sensitive information.
Certificate Authority (CA)
Certificate Authorities play a vital role by issuing digital certificates that link a signer’s identity to their public key. These certificates verify the authenticity of the signer and protect against impersonation, ensuring trust in the system.
Digital Fingerprint
A hash value acts as a unique digital fingerprint for the document. Any modification to the document invalidates this fingerprint, ensuring that tampering is immediately detectable.
Hashing Algorithm
Advanced hashing algorithms like SHA-256 transform data into a secure, fixed-length representation. These algorithms are irreversible, which means it is impossible to reconstruct the original data from the hash value, ensuring the document’s security.
Encryption and Decryption
The encryption of the hash value with the signer’s private key creates the digital signature, while decryption using the public key allows recipients to verify the document’s authenticity and integrity.
Benefits of Using Digital Signatures
Digital signatures offer numerous advantages that make them indispensable in a paperless world. By streamlining processes and ensuring security, they are transforming how organizations and individuals manage their digital transactions.
Enhanced Security
Digital signatures provide unparalleled security by ensuring data integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. The use of encryption and hashing makes them tamper-proof and resistant to fraud, providing confidence in their validity.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Eliminating the need for physical documents reduces costs associated with printing, signing, and shipping. Additionally, digital signatures enable instant approvals and transactions, saving time for all parties involved.
Eco-Friendly
By reducing reliance on paper, ink, and physical transportation, digital signatures contribute to environmental sustainability. They help organizations align with global eco-friendly practices and reduce their carbon footprint.
Legal Validity
Digital signatures are legally recognized under various regulations, including the eSign Act (USA), eIDAS (EU), and IT Act (India). This ensures that they are compliant and trustworthy for signing contracts, legal documents, and more.
Scalability
Whether it’s signing contracts, securing emails, or authenticating software, digital signatures can scale to meet the needs of individuals, small businesses, and large enterprises alike, offering versatility across applications.
Conclusion
In a world that is rapidly embracing digital transformation, digital signatures have become an essential tool for ensuring secure and authentic paperless transactions. By combining cryptographic techniques with trusted certificate authorities, digital signatures offer a reliable, efficient, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods of signing and verifying documents.
Understanding and adopting digital signatures will empower organizations and individuals to confidently navigate the digital landscape. Whether you’re signing contracts, verifying identities, or securing sensitive data, digital signatures provide the foundation for a secure and seamless digital future.
What is a Digital Signature?
In an increasingly paperless world, digital signatures are revolutionizing the way we authenticate documents and messages. These electronic signatures serve as a secure, tamper-proof method for verifying the origin and content of digital information. By leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques, digital signatures provide a reliable means of maintaining trust and security, ensuring that documents remain authentic and unaltered throughout their lifecycle.
How Do Digital Signatures Work?
Understanding how digital signatures function requires a closer look at the cryptographic techniques that make them secure and trustworthy. These signatures rely on a combination of public and private keys, along with hashing algorithms and encryption methods, to ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital content.
Key Pair Generation
Each user is issued a unique pair of cryptographic keys: a private key, which is confidential, and a public key, which is shared with others. This pair works together to create and verify digital signatures, ensuring security and authenticity.
Hashing Algorithm
Before a document is signed, its contents are processed through a hashing algorithm, which generates a unique fixed-length hash value. Any alteration to the document’s content results in a completely different hash value, safeguarding the document’s integrity.
Encryption with Private Key
The hash value generated from the document is encrypted using the signer’s private key, creating the digital signature. This ensures that only the signer could have created the signature, verifying its authenticity.
Verification Process
To verify a digital signature, the recipient decrypts the signature using the signer’s public key. They then generate a new hash from the document and compare it to the decrypted hash. If the two hashes match, the document is confirmed as authentic and unchanged.
How Digital Signatures Ensure Paperless Security
Digital signatures employ a combination of cryptographic principles and trusted entities to ensure secure, paperless transactions. Here’s how these elements contribute to their effectiveness:
Public Key and Private Key
The use of a private key for creating the signature and a public key for verification ensures that documents remain secure and that the authenticity of the signer is upheld without compromising sensitive information.
Certificate Authority (CA)
Certificate Authorities play a vital role by issuing digital certificates that link a signer’s identity to their public key. These certificates verify the authenticity of the signer and protect against impersonation, ensuring trust in the system.
Digital Fingerprint
A hash value acts as a unique digital fingerprint for the document. Any modification to the document invalidates this fingerprint, ensuring that tampering is immediately detectable.
Hashing Algorithm
Advanced hashing algorithms like SHA-256 transform data into a secure, fixed-length representation. These algorithms are irreversible, which means it is impossible to reconstruct the original data from the hash value, ensuring the document’s security.
Encryption and Decryption
The encryption of the hash value with the signer’s private key creates the digital signature, while decryption using the public key allows recipients to verify the document’s authenticity and integrity.
Benefits of Using Digital Signatures
Digital signatures offer numerous advantages that make them indispensable in a paperless world. By streamlining processes and ensuring security, they are transforming how organizations and individuals manage their digital transactions.
Enhanced Security
Digital signatures provide unparalleled security by ensuring data integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. The use of encryption and hashing makes them tamper-proof and resistant to fraud, providing confidence in their validity.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Eliminating the need for physical documents reduces costs associated with printing, signing, and shipping. Additionally, digital signatures enable instant approvals and transactions, saving time for all parties involved.
Eco-Friendly
By reducing reliance on paper, ink, and physical transportation, digital signatures contribute to environmental sustainability. They help organizations align with global eco-friendly practices and reduce their carbon footprint.
Legal Validity
Digital signatures are legally recognized under various regulations, including the eSign Act (USA), eIDAS (EU), and IT Act (India). This ensures that they are compliant and trustworthy for signing contracts, legal documents, and more.
Scalability
Whether it’s signing contracts, securing emails, or authenticating software, digital signatures can scale to meet the needs of individuals, small businesses, and large enterprises alike, offering versatility across applications.
Conclusion
In a world that is rapidly embracing digital transformation, digital signatures have become an essential tool for ensuring secure and authentic paperless transactions. By combining cryptographic techniques with trusted certificate authorities, digital signatures offer a reliable, efficient, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods of signing and verifying documents.
Understanding and adopting digital signatures will empower organizations and individuals to confidently navigate the digital landscape. Whether you’re signing contracts, verifying identities, or securing sensitive data, digital signatures provide the foundation for a secure and seamless digital future.

Issue Digital Credetials, Certificate, marksheet instant with Secure Blockchain Technology.

Issue Digital Credetials, Certificate, marksheet instant with Secure Blockchain Technology.

Issue Digital Credetials, Certificate, marksheet instant with Secure Blockchain Technology.
Read More Blogs
Read More Blogs
Read More Blogs

Why Digital Credentials Are Becoming a Global Standard for Skill Recognition
27 Feb 2025
how to validate digital signature in certificate online
27 Feb 2025
how to download Issued certificate from digilocker
5 Feb 2025
